
Apollo Guide
Apollo 11 Landing Site

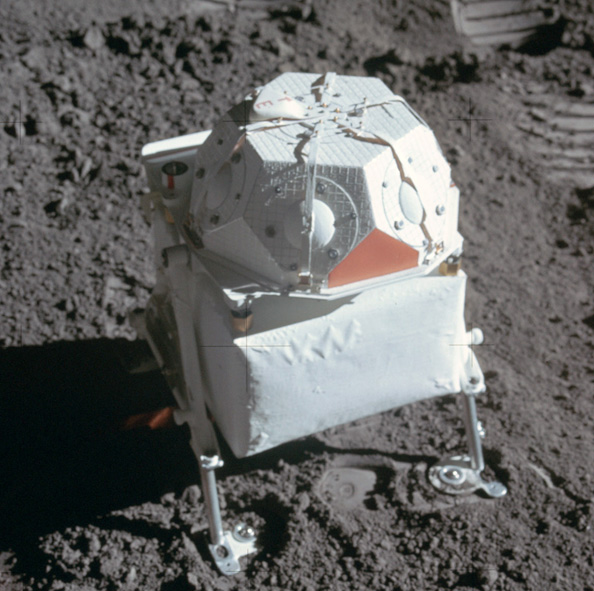
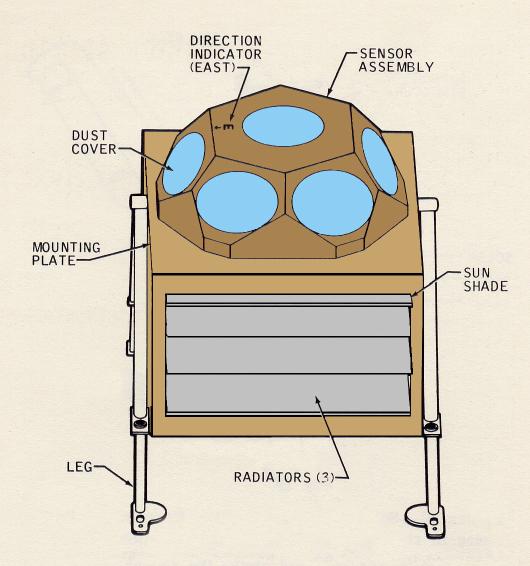
Solar Wind Spectrometer
Measures the solar wind at the lunar surface, the general properties of the solar wind, and its interaction with the Moon.
The solar wind is composed of matter ejected continuously from the Sun that spreads throughout the Solar System. The energy, density, direction of travel, and its variations were measured by the SWS. Seven sensors were located under dust shields, allowing a study of the solar wind at the lunar surface, the general properties of the solar wind and its interaction with the Moon. The solar wind stretches the Earth’s magnetic field out behind the Earth, beyond the Moon’s orbit, so the SWS also studied the Earth’s magnetic tail when the Moon passed through it. The SWS found the solar wind behaved the same as in free space outside the Earth’s magnetic tail and is slightly disturbed in the geomagnetic transition region.
.
Non - Normal
An unexpected problem with the first ALSEP on Apollo 12 involved the cables that connected the various experiment modules to the Central Station. Although the cables were fairly stiff, on Earth they tended to lie flat to the ground, held down by their own weight. However, on the Moon, the cables hardly seemed to notice the one sixth gravity and retained loops and bends they had acquired during storage inside the LM - loops that stood up from the ground rather like sections of a frozen garden hose. There were no disastrous tripping episodes during Apollo 12 such as occurred on Apollo 16, but the need to dodge cable loops slowed the astronaut's work.
|
|
|
Home / Acronyms / Index / Schematics / Systems
Operations / Non-Normal / Normal
Panels / 1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 / 8 / 12 /14
Copyright 2024 APOLLO 11 GUIDE©